The way individuals think about their intelligence, abilities, and potential can significantly impact their success. Mindset Theory, developed by psychologist Carol Dweck, explains how our beliefs about intelligence and growth shape learning, achievement, and personal development.
By understanding mindset theory, educators, parents, and students can develop strategies to enhance motivation, resilience, and long-term success. This article explores the role of attitude in learning, the difference between fixed and growth mindsets, and strategies to cultivate a growth-oriented approach.
What is Mindset Theory?

🔹 Mindset Theory explains how people perceive their abilities and intelligence, affecting their motivation, effort, and resilience.
🔹 Carol Dweck identified two primary types of mindsets:
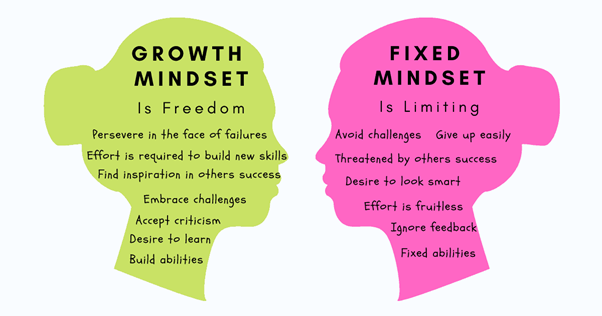
- Fixed Mindset – Believing that intelligence and abilities are static.
- Growth Mindset – Believing that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and persistence.
📍 Students with a growth mindset are more likely to embrace challenges and persist through difficulties, leading to higher achievement.
Fixed Mindset vs. Growth Mindset
| Aspect | Fixed Mindset 🛑 | Growth Mindset ✅ |
|---|---|---|
| View on Intelligence | Intelligence is innate and unchangeable. | Intelligence can be developed with effort. |
| Response to Challenges | Avoids challenges to protect self-image. | Embraces challenges as opportunities to grow. |
| Reaction to Failure | Sees failure as a reflection of ability. | Sees failure as a learning experience. |
| Effort & Persistence | Avoids effort if success isn’t guaranteed. | Values effort as a key to mastery. |
| Response to Feedback | Takes criticism personally. | Uses feedback to improve. |
| Attitude Toward Others’ Success | Feels threatened by others’ success. | Finds inspiration in others’ success. |
📍 Shifting from a fixed to a growth mindset transforms how students approach learning and achievement.
How Mindset Affects Learning & Achievement
1. Motivation & Engagement 🎯
✔ Growth mindset students are more motivated to learn and take academic risks.
✔ They see challenges as opportunities, not obstacles.
📖 Example: A student struggling with math may view it as “I’m just bad at math” (fixed mindset) or “I can improve with practice” (growth mindset).
2. Resilience & Grit 💪
✔ Growth mindset fosters perseverance through difficulties.
✔ Students become more adaptable to setbacks and failures.
📖 Example: A musician who practices despite struggling with a difficult piece believes that effort leads to progress.
3. Academic Performance & Success 📚
✔ Growth mindset students tend to achieve higher grades and develop better problem-solving skills.
✔ Fixed mindset students may give up easily, leading to lower academic outcomes.
📖 Example: Research shows that growth mindset interventions improve performance in subjects like math and science.
How to Develop a Growth Mindset
1. Emphasize Effort Over Talent 🔄
✔ Praise hard work and persistence, not just intelligence.
✔ Shift language from “You’re so smart!” to “I love how hard you worked on this!”
📍 Effort-driven praise builds confidence and resilience.
2. Reframe Failure as Learning 🏆
✔ Encourage students to see mistakes as feedback.
✔ Teach reflection and problem-solving instead of fear of failure.
📍 Failure is not a permanent state—it’s part of progress.
3. Teach Neuroplasticity 🧠
✔ Explain how the brain grows stronger with learning.
✔ Show students that intelligence is not fixed but expandable.
📍 Understanding brain growth empowers students to take charge of their learning.
4. Model Growth Mindset as Educators & Parents 👨🏫
✔ Use phrases like “I’m still learning” and “I can improve”.
✔ Demonstrate resilience when facing challenges.
📍 Adults who model a growth mindset encourage the same in students.
5. Encourage Challenge-Seeking Behavior 🏗
✔ Promote activities that require problem-solving and persistence.
✔ Shift focus from perfection to progress.
📖 Example: Encourage students to take on advanced coursework or new hobbies even if success isn’t guaranteed.
6. Provide Constructive Feedback ✍️
✔ Give feedback focused on growth and improvement.
✔ Avoid labeling students as “smart” or “talented”—instead, highlight effort and strategy.
📖 Example: Instead of “You’re a great writer,” say “Your storytelling has improved because of your descriptive details.”
Real-World Applications of Mindset Theory
🚀 Education: Schools implementing growth mindset programs see higher student engagement and performance.
💼 Business & Leadership: Growth mindset employees are more innovative and adaptable.
🏆 Sports & Performance: Athletes with a growth mindset train harder and recover from setbacks faster.
🧠 Personal Development: Helps individuals overcome self-doubt and achieve long-term goals.
📍 Mindset theory is applicable beyond education—it influences success in all areas of life.
Final Thoughts: Mindset Shapes Success
Mindset is a powerful determinant of learning and achievement. By cultivating a growth mindset, students and professionals alike can develop resilience, embrace challenges, and unlock their full potential knowledge.
🔥 What strategies have helped you develop a growth mindset? Share your experiences below! 🚀📚